Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –
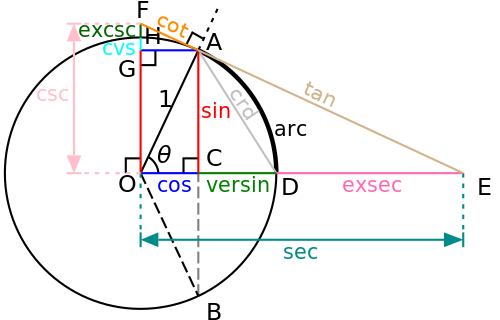
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that Ewa Ligocka cooked another mathematician's goose?
- ... that Catechumen, a Christian first-person shooter, was funded only in the aftermath of the Columbine High School massacre?
- ... that owner Matthew Benham influenced both Brentford FC in the UK and FC Midtjylland in Denmark to use mathematical modelling to recruit undervalued football players?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that Ukrainian baritone Danylo Matviienko, who holds a master's degree in mathematics, appeared as Demetrius in Britten's opera A Midsummer Night's Dream at the Oper Frankfurt?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
More did you know –

- ...that it is impossible to devise a single formula involving only polynomials and radicals for solving an arbitrary quintic equation?
- ...that Euler found 59 more amicable numbers while for 2000 years, only 3 pairs had been found before him?
- ...that you cannot knot strings in 4 dimensions, but you can knot 2-dimensional surfaces, such as spheres?
- ...that there are 6 unsolved mathematics problems whose solutions will earn you one million US dollars each?
- ...that there are different sizes of infinite sets in set theory? More precisely, not all infinite cardinal numbers are equal?
- ...that every natural number can be written as the sum of four squares?
- ...that the largest known prime number is nearly 41 million digits long?
Selected article –
 |
| A labeled graph on 6 vertices and 7 edges Image credit: User:Booyabazooka |
Informally speaking, a graph is a set of objects called points, nodes, or vertices connected by links called lines or edges. In a proper graph, which is by default undirected, a line from point A to point B is considered to be the same thing as a line from point B to point A. In a digraph, short for directed graph, the two directions are counted as being distinct arcs or directed edges. Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots (for the points, vertices, or nodes), joined by curves (for the lines or edges). Graphs have applications in both mathematics and computer science, and form the basic object of study in graph theory.
Applications of graph theory are generally concerned with labeled graphs and various specializations of these. Many problems of practical interest can be represented by graphs. The link structure of a website could be represented by a directed graph: the vertices are the web pages available at the website and a directed edge from page A to page B exists if and only if A contains a link to B. A graph structure can be extended by assigning a weight to each edge of the graph. Graphs with weights, or weighted graphs, are used to represent structures in which pairwise connections have some numerical values. For example if a graph represents a road network, the weights could represent the length of each road. A digraph with weighted edges in the context of graph theory is called a network. Networks have many uses in the practical side of graph theory, network analysis (for example, to model and analyze traffic networks). (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus